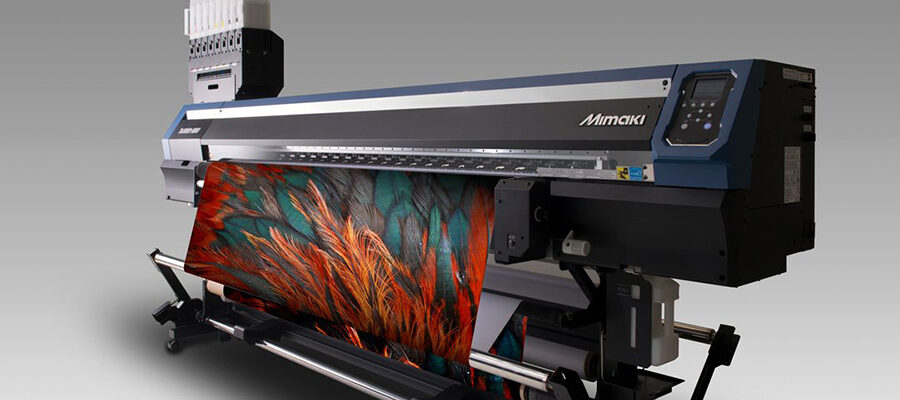
Digital Textile Printing, ITNH Explains the Basics
• Natural fibers like cotton: Reactive dyes
• Polyester: Disperse dyes
• Nylon and silk: Acid dyes
To find the right ink type, make sure you know what fabrics you will be printing on first. From there, you can determine the appropriate ink for the fabric. There’s no “silver bullet” ink type. This, combined with the high probability that you won’t purchase multiple printers (to run different inks sets), means that it is important to prioritize. Think about which fabrics and fiber types are most important in your business plan and start there. Then you can build your fabric printing business by adding additional printing technology. It’s a smart idea to work with an industry expert who can help you strategize the best initial equipment package to make future decisions easier. Fabric Construction In addition to the different material types, fabrics can be constructed as:• Woven
• Non-woven
• Circular knit
• Warp knit
The construction of the fabric for your intended application will lead you to the best printing equipment. Woven and non-woven fabrics typically only require a basic fabric printer with proper fabric tensioning and traditional pinch-rollers to advance the fabric through the printer. But knit fabrics can be a bit more difficult to work with. Knit materials can be stretchy and curl during the print process, so you should look for printers that include a sticky “transport” belt. With this feature, the fabric will be pressed flat against the belt and will be peeled off and wound once it exits the printer. These printers may have a higher cost than basic machines, but this is the most practical option for printing on difficult knit fabrics and other delicate fabrics. Textile Printing Process Example There are variances to the overall process of printing textiles. When the details of the fabric, ink, and printer type have all been decided, the process will be identified, and the equipment package can be finalized. It is important to work with an industry professional to make sure that the correct process is identified with the correct processing equipment. However, here is an example of the steps involved in printing on nylon:1. Coat the fabric with the specific coating to receive acid dye
a. Or, you can purchase fabric that’s already coated
2. Print fabric using the best-suited printer
3. Steam fabric in a textile steamer for ink fixation (permanence)
4. Wash fabric in a washing machine to remove pre-coat and excess/unfixed ink
Other processes, like those for polyester, usually have fewer steps than printing on nylon. Just keep in mind that each process will require specific equipment to achieve the best results. The Steps to Finding the Perfect Digital Textile Printing Package1. Identify the type of fabrics you’ll be working with. Make sure to pay attention to the construction of the fabric.
2. Check what ink type is best for your fabric.
3. Understand the printing process for your specific application.
4. Find a printer that works with your intended fabric and ink.
5. Explore the additional equipment you might need, like a pre-treatment machine, steamer, or heat press.
Since digital textile printing can be a complex process depending on your application, it’s always recommended that you talk to a professional before investing your money in any equipment. The fabric types, ink chemistries, materials, and processes vary to an extreme, but a professional can guide you through the pros and cons of your options. With the right equipment, you’ll be on your way to textile printing success in no time. For additional information, contact Mike Terlizzi, Managing Partner, ITNH, Inc.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]Share this post
Author
DESIGN/COLOR TRENDS AND AWESOME INFORMATION IN YOUR INBOX
Sign up for our monthly trend letter